Streamlit vs. MecSimCalc

Streamlit and MecSimCalc both offer solutions to simplify app development and data visualization with Python. However, they cater to different user bases and provide unique features. In this article, we'll delve into a detailed comparison between Streamlit and MecSimCalc.
Overview
Let's start with an overview of both platforms.
| Feature | Streamlit | MecSimCalc |
|---|---|---|
| Website | Streamlit | MecSimCalc |
| Description | "A faster way to build and share data apps. Streamlit turns data scripts into shareable web apps in minutes. All in pure Python. No front‑end experience required." | "The simplest way to build and share computational tools. Create and share your Python web apps in minutes for free." |
| Target Audience | Python developers, e.g. data scientists and machine learning engineers | Non-developers, e.g. engineers, consultants, educators, researchers, etc. |
| Required Knowledge | Python, Terminal, GitHub, Markdown, Streamlit library | Python |
| Ideal Use Case | Data visualization | Computational simulation and calculation |
| Cost | Free | Free |
Features Comparison
Now, let's explore the specific features and functionalities of both Streamlit and MecSimCalc.
| Feature | Streamlit | MecSimCalc |
|---|---|---|
| Documentation | docs.streamlit.io | docs.mecsimcalc.com |
| Blog | blog.streamlit.io | docs.mecsimcalc.com/blog |
| Discourse Forum | streamlit.io/community | community.mecsimcalc.com |
| Custom Code Syntax | Yes, requires custom streamlit functions | No, works with plain Python |
| Resource Limits | 1 GB RAM, sleeps after 7 days of inactivity | 7 days, 16 vCPUs, 120 GB RAM, 200GB disk space |
| No Download Required | ❌ | ✅ |
| Online Editor | ❌ | ✅ |
| Monetize Apps | ❌ | ✅ |
| Conditional Inputs | ✅ | ✅ |
| Dynamic Tables | ✅ | ✅ |
| Interactivity & Animations | ✅ | ❌ |
| Plotting | ✅ | ✅ |
| Maps | ✅ | ✅ |
| Embeddable | ✅ | ✅ |
| Drag-and-drop interface | ❌ | ✅ |
| Run in Background | ❌ | ✅ |
The Workflow
Next, we will briefly explore the workflow of both Streamlit and MecSimCalc, from creating an app to deploying it.
Streamlit
Internally, Streamlit uses Tornado as its web server. Streamlit communicates with websockets, making it suitable for interactive real-time applications. [source]
Here is a simplified workflow for creating and deploying a basic Streamlit app:
Step 1: Download and start streamlit via the terminal:
# Prerequisite: download Python and pip, if not already installed
pip install streamlit
touch my_app.py
streamlit run my_app.py
After running streamlit run, a new tab will open on your browser with the app running at a localhost url. All the coding will be done locally on your computer and edits in my_app.py will automatically be reflected in the browser.
Step 2: Write the Streamlit code inside my_app.py. Refer to Streamlit docs for custom streamlit functions required to build the interface and layout.
# my_app.py
import streamlit as st
st.write("# a+b")
col1, col2, col3 = st.columns([6, 1, 6])
with col1:
a = st.number_input("a", value=12)
with col2:
st.write("# +")
with col3:
b = st.number_input("b", value=34)
sum = a + b
product = a * b
st.write("The sum of the two numbers is " + str(sum))
st.write("The product of the two numbers is " + str(product))
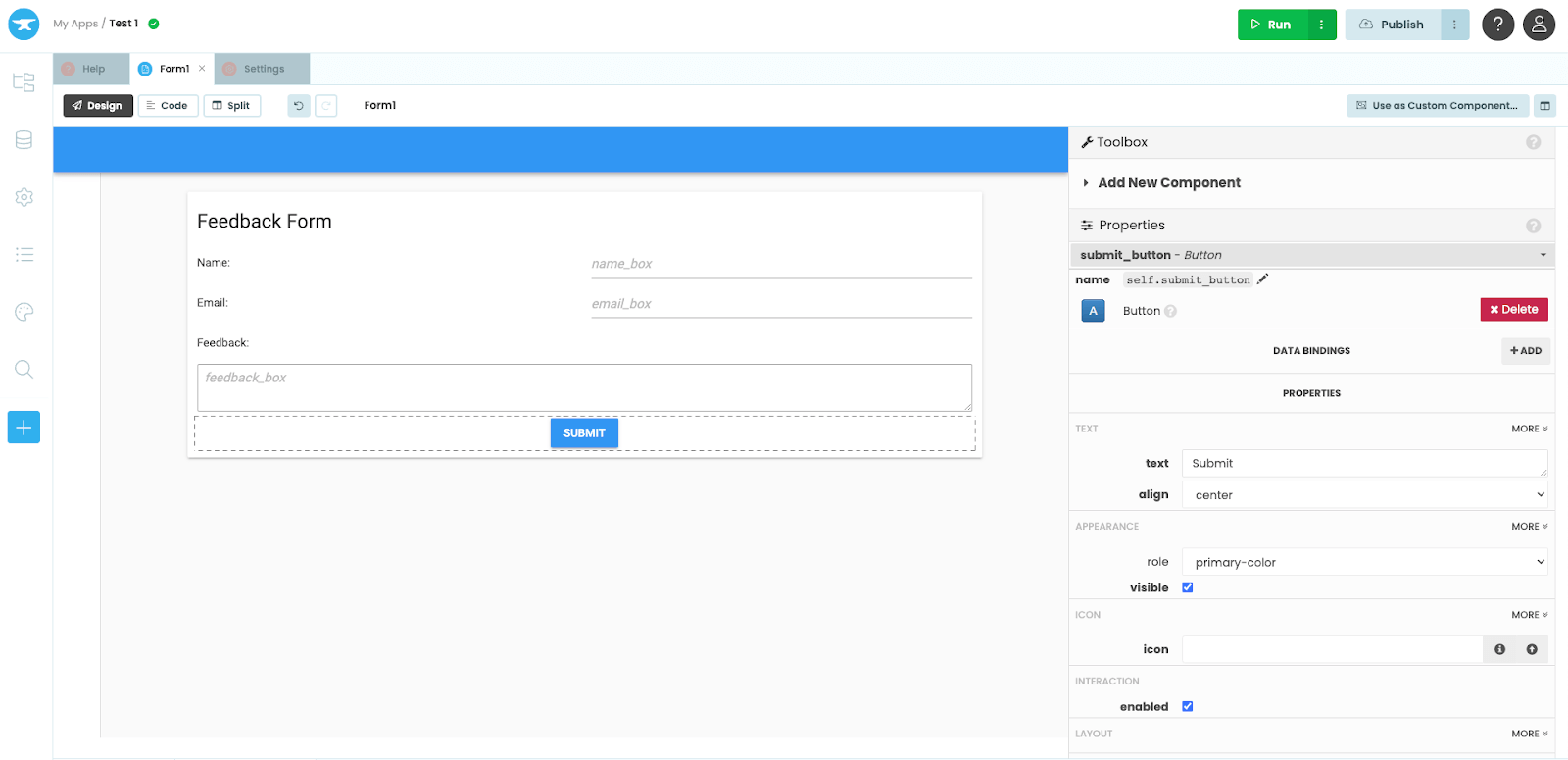
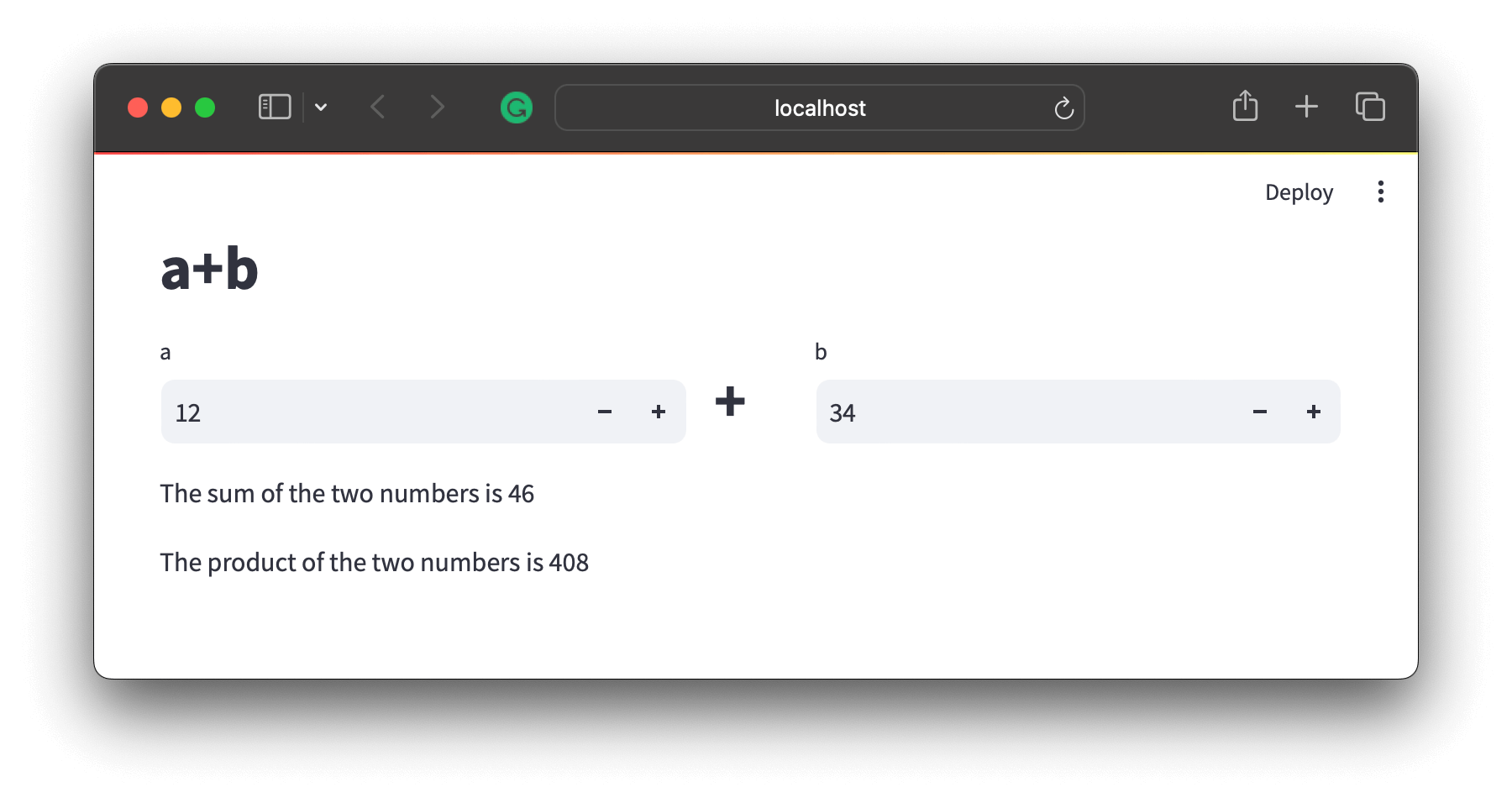
Step 3: The inputs, code, and outputs are all handled in the single Python file. The localhost webpage looks like this:
Step 4: Before deploying the app, a Github account is required and then create a new Github repository. Save the code to this repository by downloading and using the Github desktop app or using the terminal:
# Prerequisite: download Git, if not already installed
git add .
git commit -m "saving my_app.py"
git push
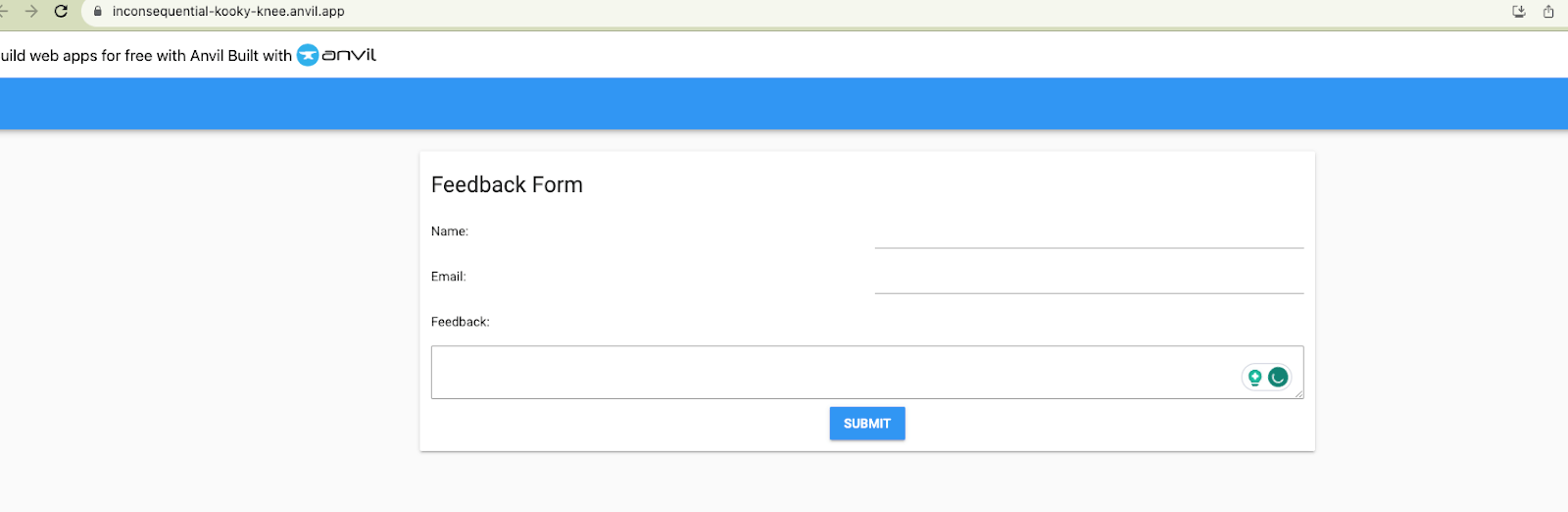
Step 5: Finally, to deploy the app, create a Streamlit Cloud account and fill out the Deploy an app form with the Github repository link. Once submitted, the app will build for a few minutes before becoming accessible at a streamlit url.
MecSimCalc
Internally, MecSimCalc uses serverless functions to run Python functions, making it suitable for computational simulations and calculations, which may require more compute power and longer runtimes.
Here is a simplified workflow for creating and deploying a basic MecSimCalc app:
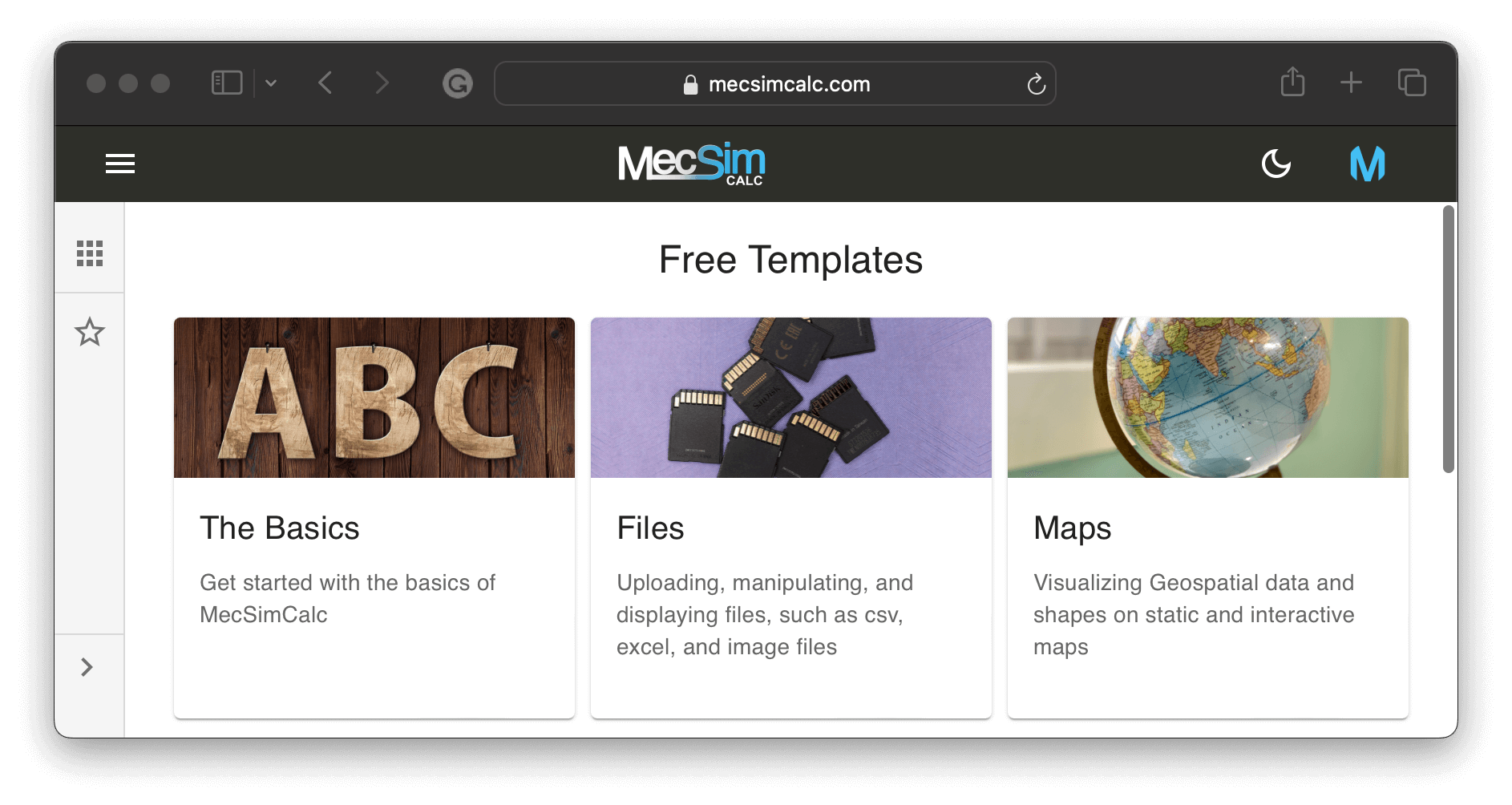
Step 1: Visit https://mecsimcalc.com/create and select one of the templates to create a new app.
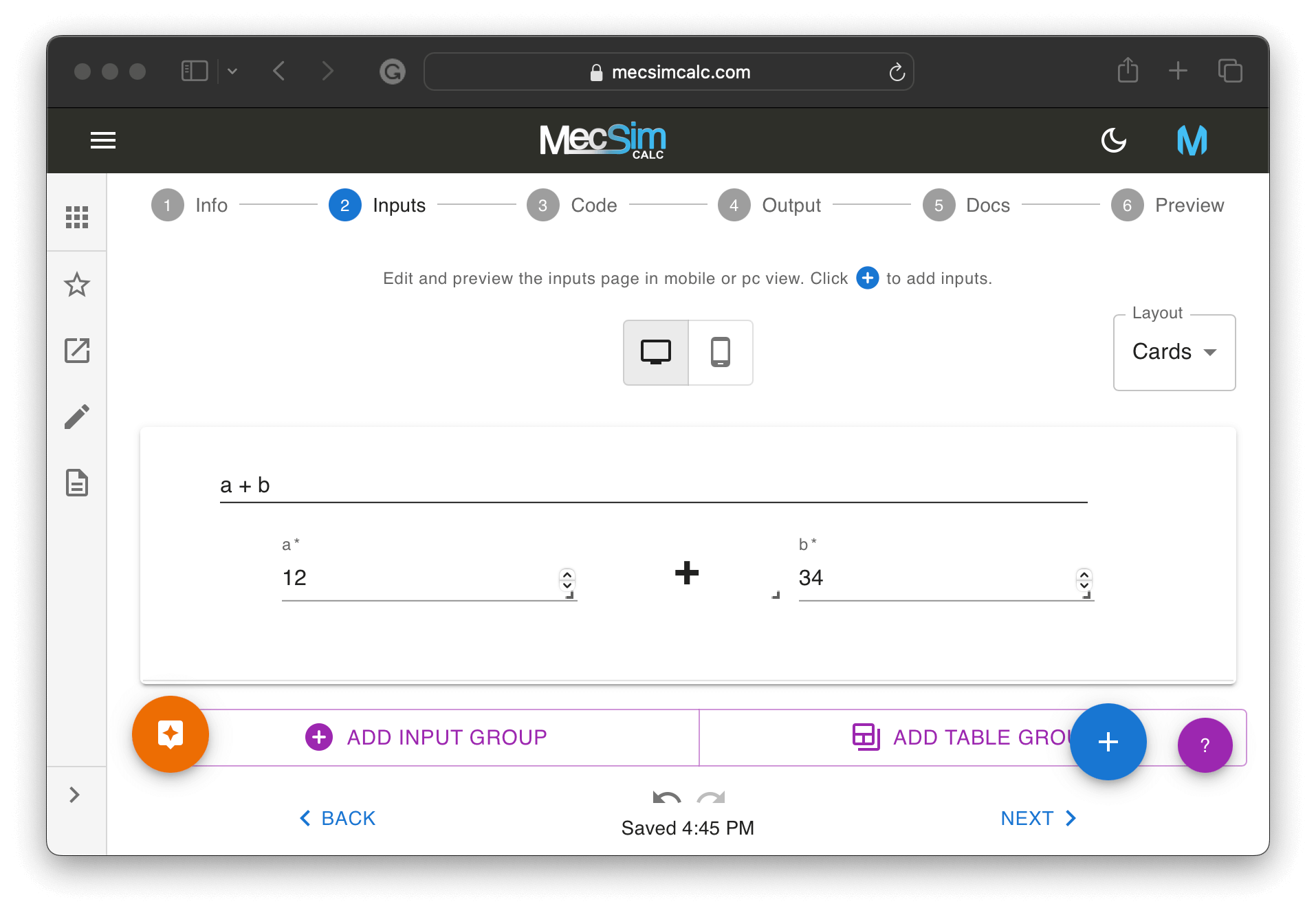
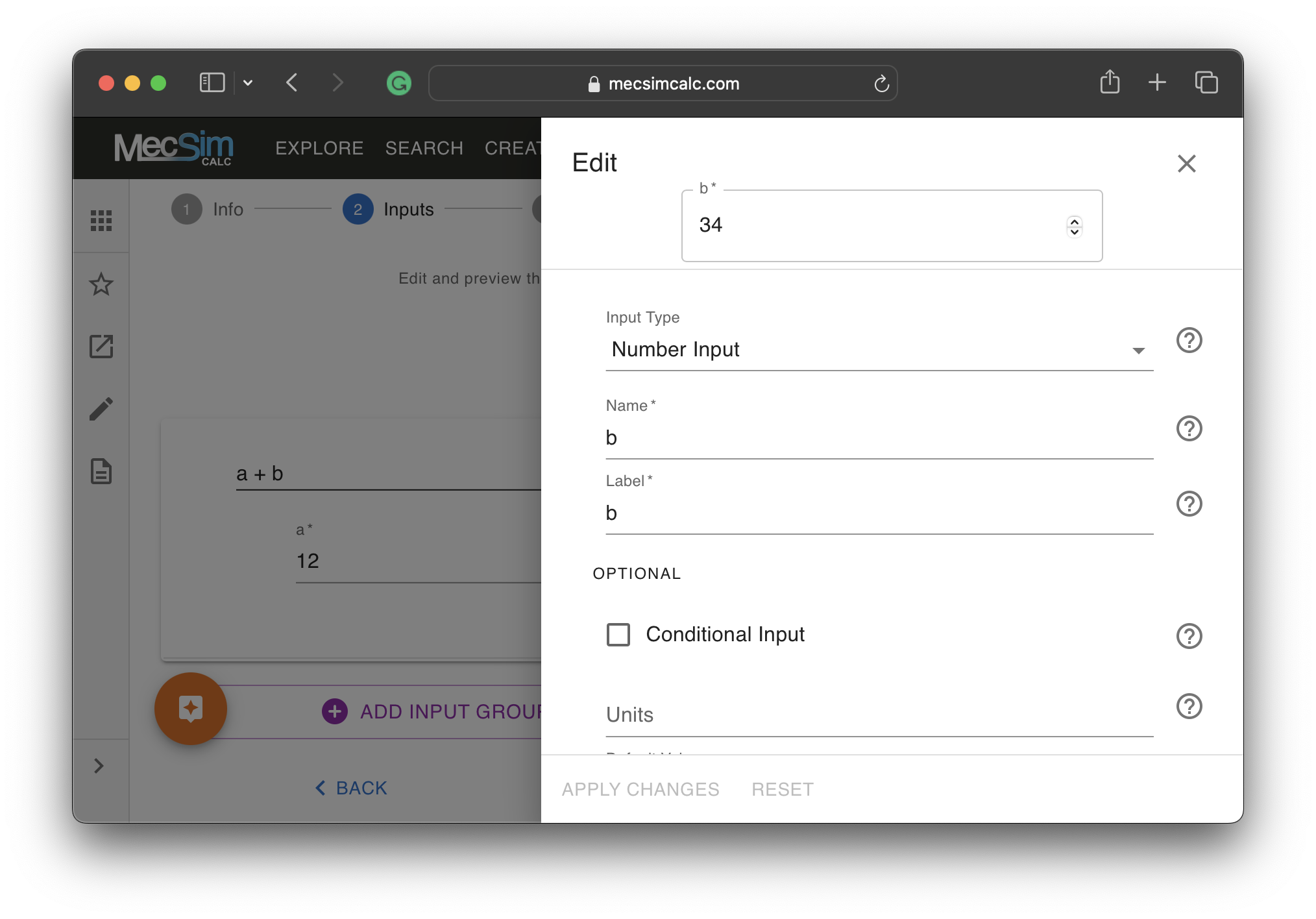
 Step 2: On the inputs step, use the drag-and-drop interface to add, position, and delete the inputs. Customize each input by clicking on it.
Step 2: On the inputs step, use the drag-and-drop interface to add, position, and delete the inputs. Customize each input by clicking on it.
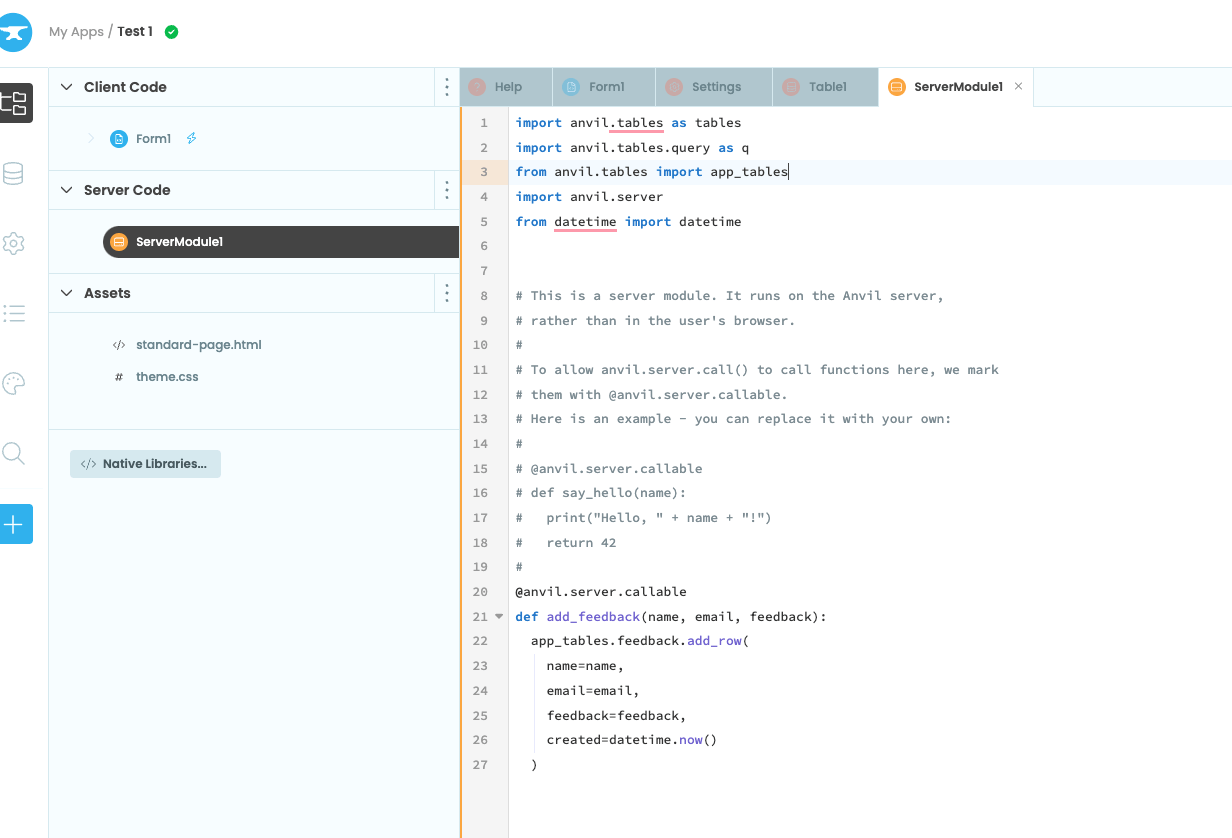
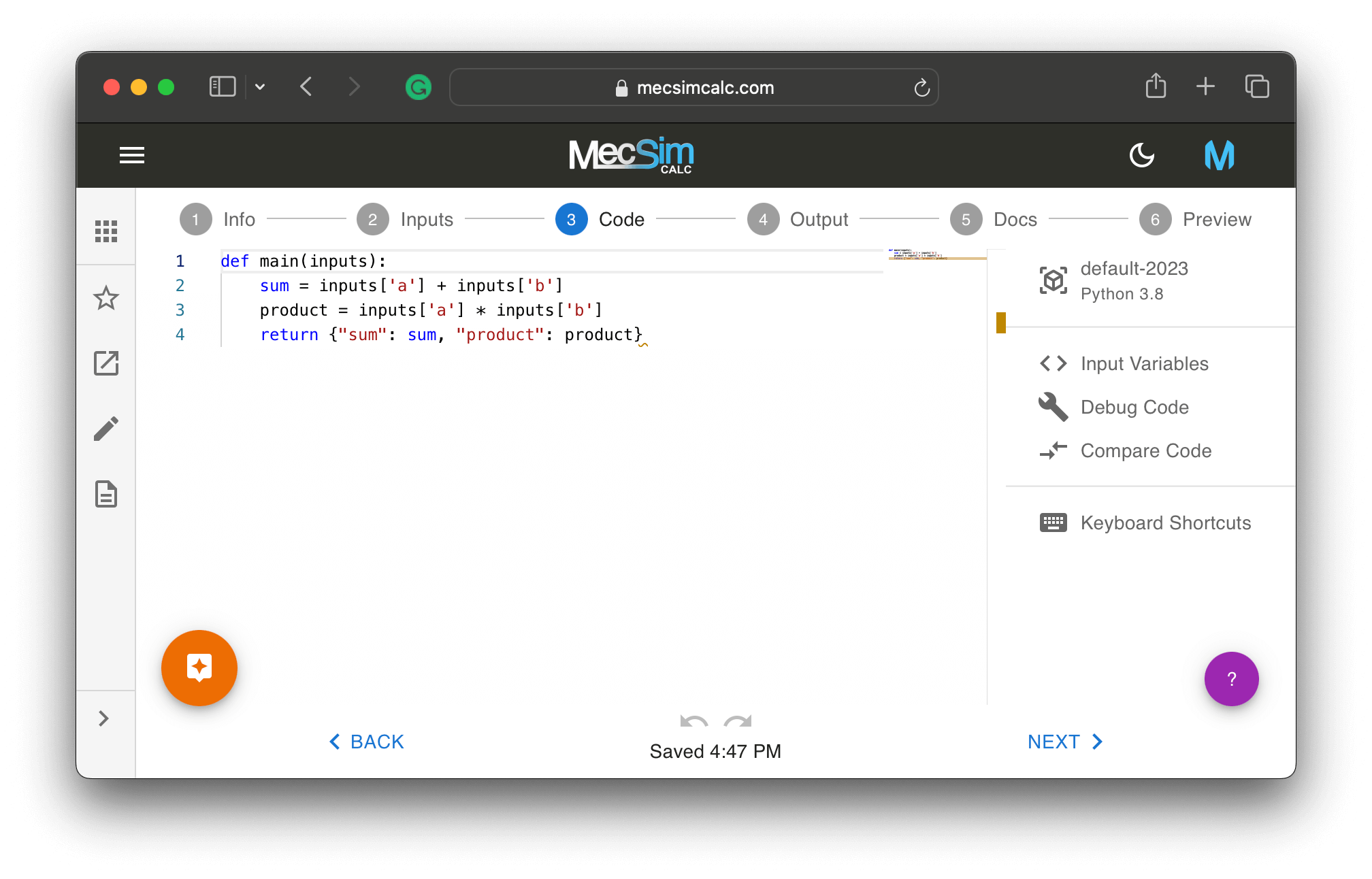
 Step 3: On the code step, write Python code that uses the
Step 3: On the code step, write Python code that uses the inputs to calculate the outputs. No need to learn new functions nor any installations. Use the toolbar on the right to install Python packages, debug the code, and list the input variables.
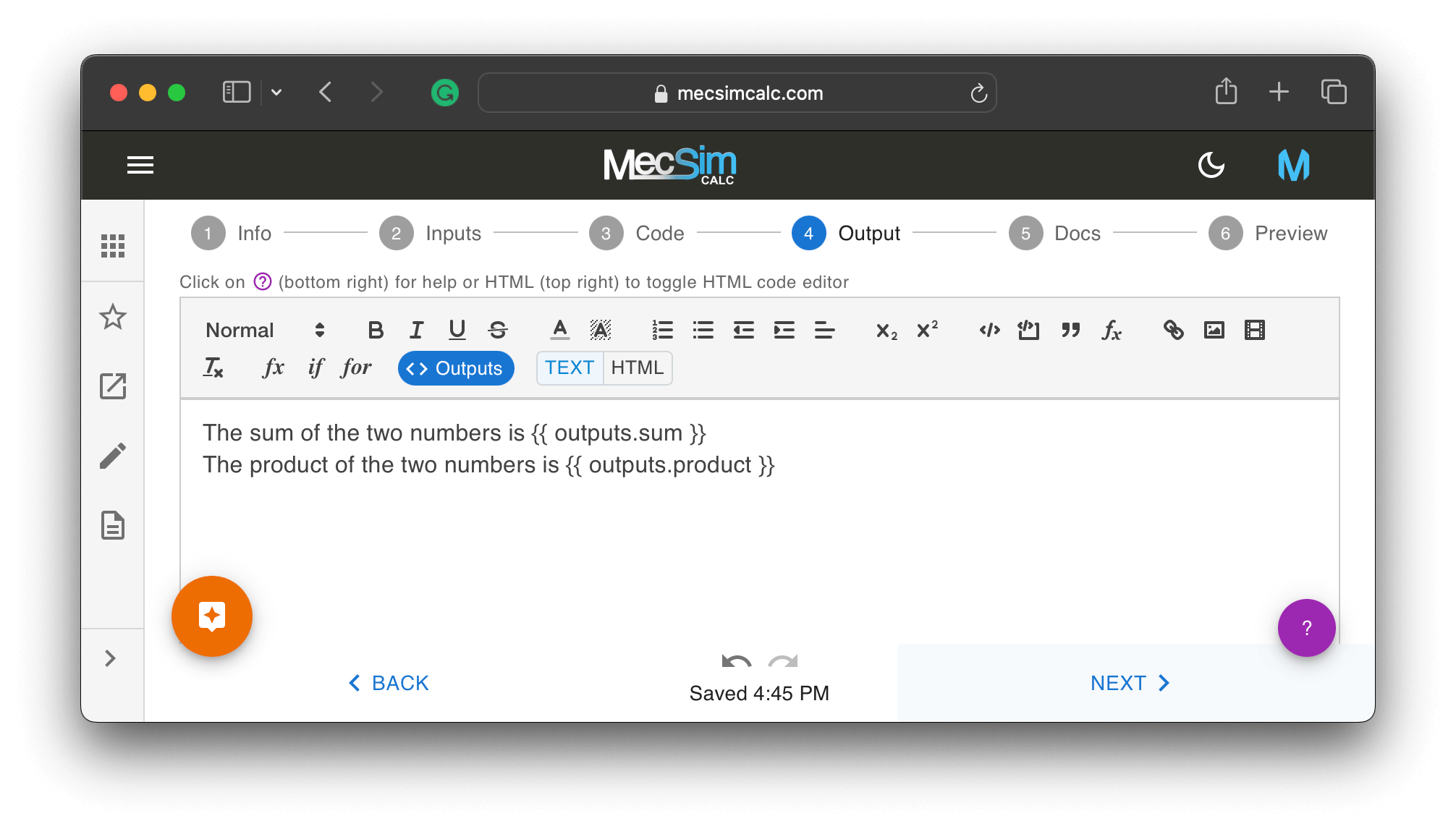
 Step 4: On the outputs step, use the rich text editor to stylize the outputs section and embed the output variables generated from the code.
Step 4: On the outputs step, use the rich text editor to stylize the outputs section and embed the output variables generated from the code.
 Step 5: Finally, to deploy the app, simply click on the Publish button at the bottom of the Preview step and the app will be accessible and searchable on MecSimCalc within a few seconds.
Step 5: Finally, to deploy the app, simply click on the Publish button at the bottom of the Preview step and the app will be accessible and searchable on MecSimCalc within a few seconds.
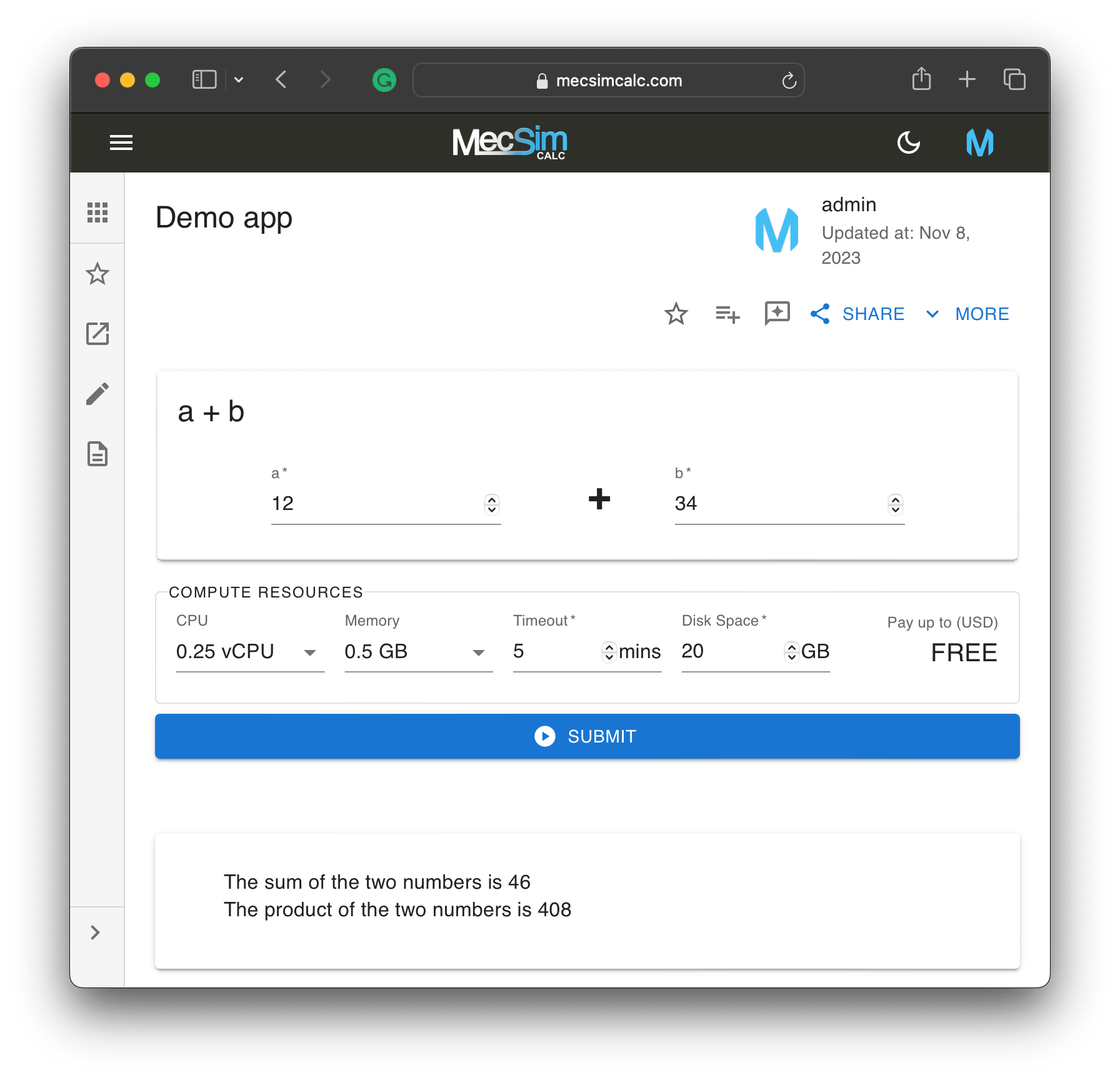
 This is what the final app looks like:
This is what the final app looks like:
Conclusion
In the realm of Python-based app development and data visualization, Streamlit and MecSimCalc offer distinct yet invaluable solutions, each tailored to different user bases and varying levels of expertise. As uncovered in this comparison, Streamlit serves the needs of Python developers, providing a platform for swiftly creating interactive data applications. However, leveraging its functionalities demands a certain level of familiarity with custom Streamlit functions and the integration of terminal/GitHub for efficient deployment. Furthermore, Streamlit is ideal for data visualization and interactive tasks, but it lacks the computational power and runtime capabilities to handle more complex simulations and calculations, that MecSimCalc has.
On the other hand, MecSimCalc carves its niche by catering to non-technical users, providing an in-browser solution that doesn't necessitate altering existing Python code. Its user-friendly interface and simplicity in operation make it an attractive choice for individuals with less technical acumen. By eliminating the requirement for comprehensive technical know-how, MecSimCalc streamlines the app development process, offering a more accessible path for those less versed in the intricacies of coding and deployment processes.
The choice between Streamlit and MecSimCalc significantly hinges on the user's level of expertise and the specific project requirements. These tools epitomize the diverse spectrum of options available for Python-based app development, each serving distinct purposes and targeting particular user demographics. Whether one opts for the developer-oriented yet feature-rich Streamlit or the user-friendly, in-browser functionality of MecSimCalc, the decision ultimately revolves around the skill set and needs of the user, showcasing the versatility of available tools in the Python ecosystem.