Working with large files
If you have a very large file that is used in your Python code, it's not recommended to copy and paste the file contents directly into your code.
Instead, it's recommended to either:
- Create a new custom code environment that contains the file.
- Host the file on an external website and then fetch it in the code at runtime.
The following instructions works for all file types.
Option 1: Custom code environment
This is the recommended way to load in large files because the file will be available instantly without having to fetch it.
Step 1: Create a new custom code environment
- Follow these instructions on building a custom environment.
- Add the large files in the Add files section.
- Once the environment is built and selected, read the file into the Python code:
with open("/home/hello.png", "r") as f:
data = f.read()
print(data)
Follow the example in this video that explains how to upload an ANN .h5 file using a custom environment:
Calling functions from an uploaded Python file
You can upload a Python file to your custom environment and use the functions in your Python code! To access the functions from the Python module simply append '/home/' to sys.path and then import all (*) from your module
import sys
sys.path.append('/home/')
from pythonModule import * // import all the functions from the external Python file
def main(inputs):
result = pythonFunction() // use a function
Check out the following short video that explains exactly how to do this!
Option 2: Fetching the file
This option is useful if you do not want to create a new custom code environment, or if you want to use a file that is already hosted on the internet. However, this option will take longer to run the code because it needs to download the file from the internet.
Step 1: Hosting the file
First, you must upload your file to a file-hosting service. You may skip this step if the file is already publicly available on the internet.
Github
Github is a very popular free-to-use website that can host your files.
- Go to github.com.
- Create an account (if you don't already have one).
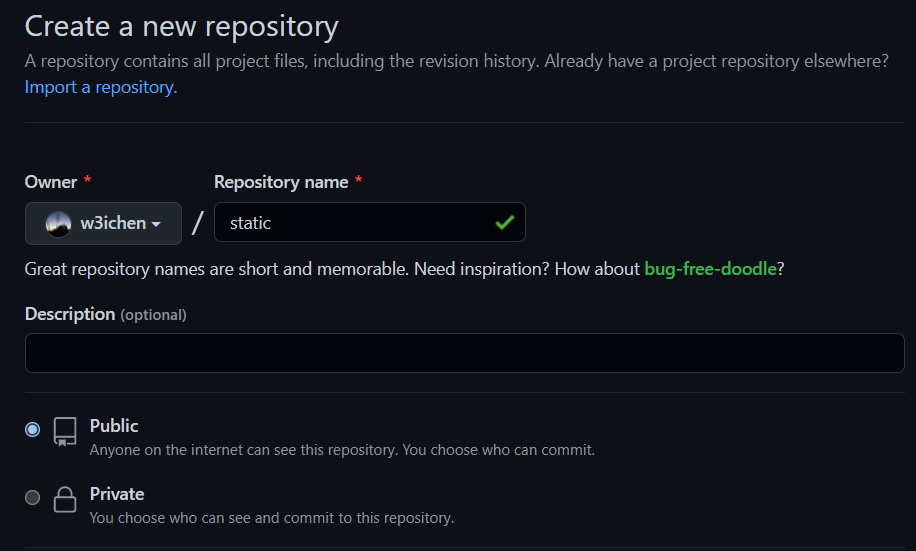
- On the homepage, click on New in the top left corner to create a new repository.
- Repositories are similar to folders that store your files.
- You can have more than one repositories. on your Github account.
- Create a new repository:
- Give your repository a name in "Repository name".
- Select Public.
- Finally, click on Create repository.
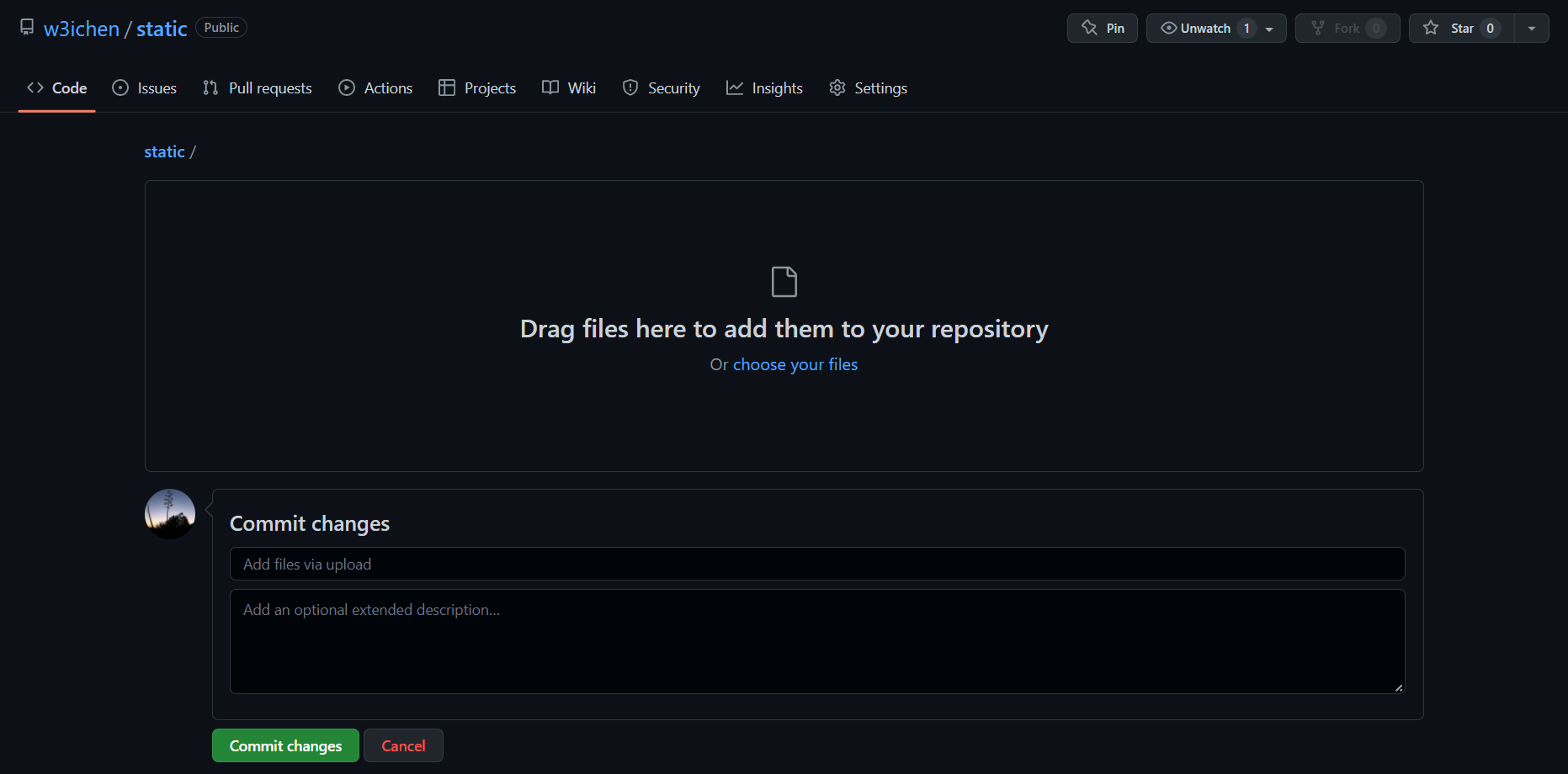
- Upload files:
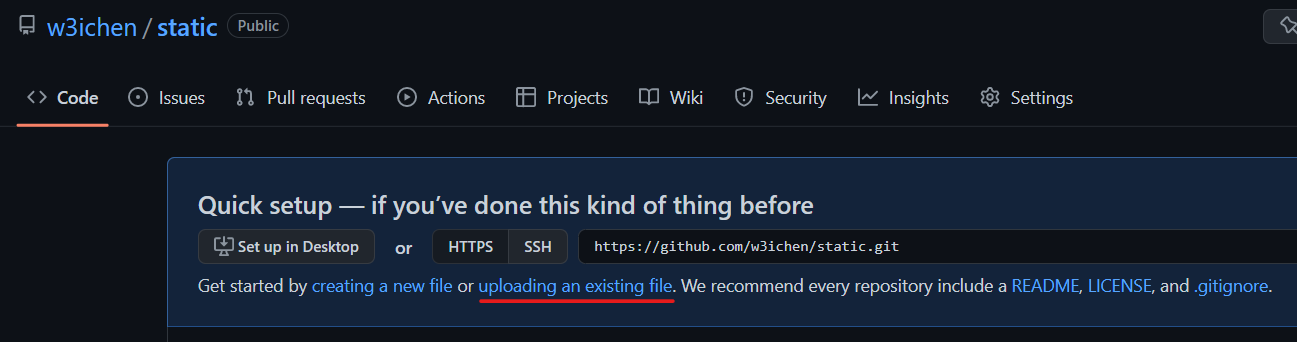
- If you see this screen, click on uploading an existing file.
- If you see this screen, click on Add file and then Upload files.
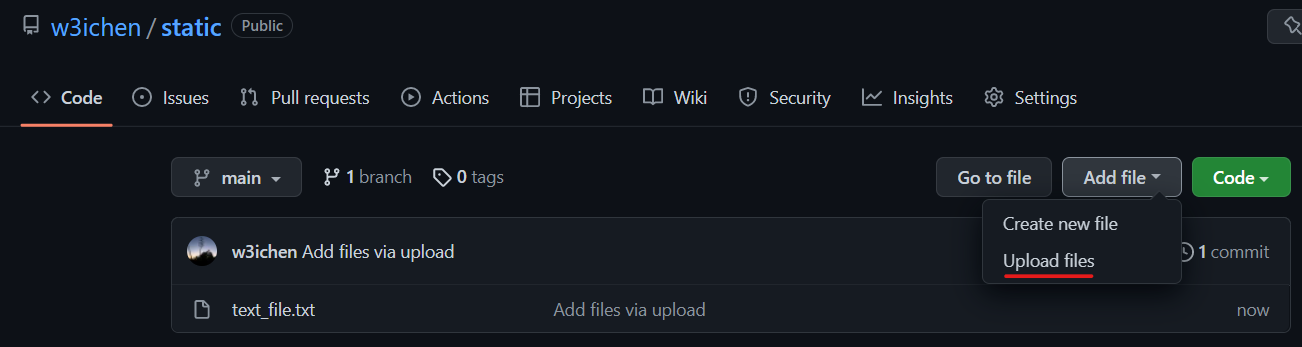
- Upload your files:
- Upload one or more files and then click on Commit changes to submit the files.
- Your uploaded files should now show up on the homepage of your repository.
- Your uploaded files are viewable at this url:
github.com/<username>/<repo name>/, where<username>is your Github username, and<repo name>is the name of the Gihub repository that your files are in. 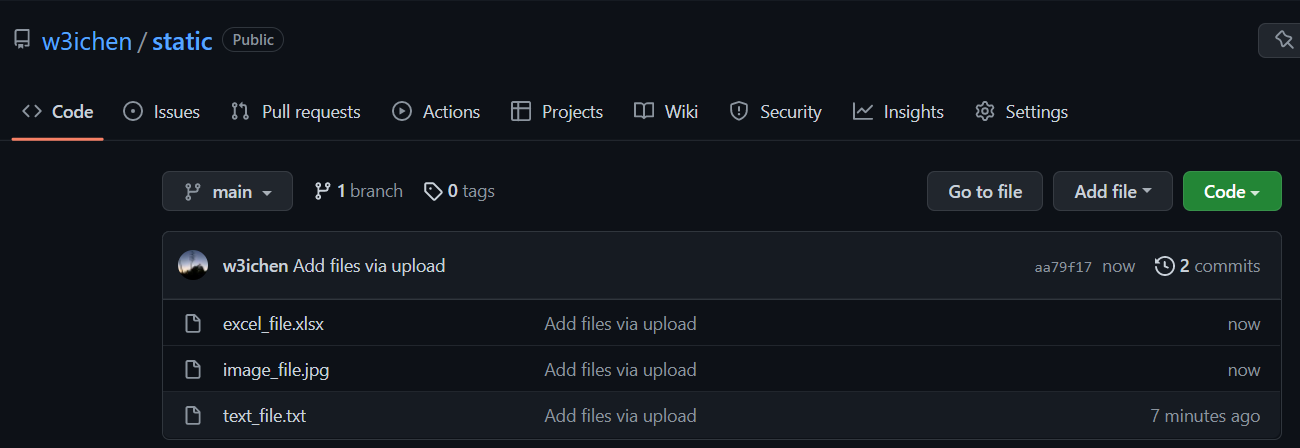
- Your uploaded files are viewable at this url:
Step 2: Getting the url
Before you can fetch the file, you need to know the url of the file, which must be publicly accessible. This url can be from any website (does not have to be from Github), the following instructions will use Github.
The url must only contain the file you want, and can not be a webpage that contains the file along with other assets, such as text and images.
Github
To fetch the url of files hosted on Github:
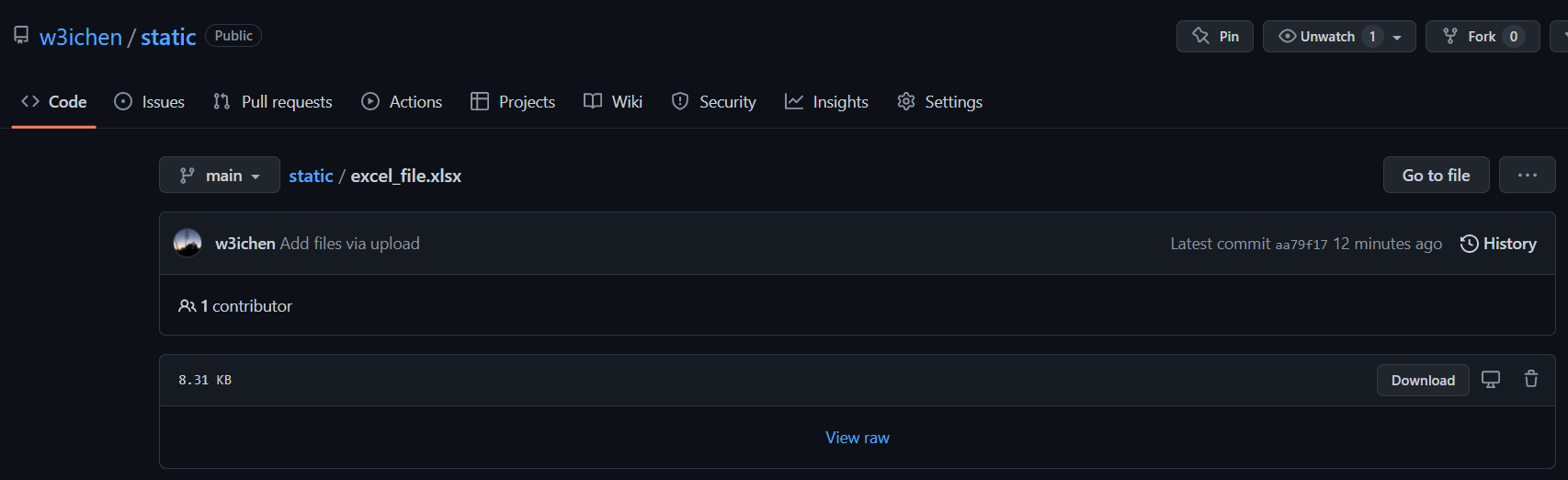
- Go to the Github repository with the files.
- Click on the filename to go to the file. For example, clicking on excel_file.xlsx:
- Copy the url of the webpage.
- For example,
https://github.com/w3ichen/static/blob/main/excel_file.xlsx
- For example,
- Add
?raw=trueto the end of the url, which references the raw data of the file.- For example,
https://github.com/w3ichen/static/blob/main/excel_file.xlsx?raw=true
- For example,
You must add ?raw=true to the end of the url for Github files
Step 3: Fetching the file
Once your file can be accessed on the web at a public url, you must first fetch the file into your Python code before you can use it. There are many different functions available depending on the type of file, that will read in a file given an url.
Text files
from urllib.request import urlopen
def main(inputs):
# Fetch file
url = "https://github.com/w3ichen/static/blob/main/text_file.txt?raw=true"
text_file = urlopen(url)
# Read entire file
lines = text_file.read().decode("utf-8")
print(lines)
return {"lines": lines}
Excel spreadsheet files
import pandas as pd
def main(inputs):
url = "https://github.com/w3ichen/static/blob/main/excel_file.xlsx?raw=true"
dataframe = pd.read_excel(url)
print(dataframe)
return {"dataframe": dataframe}
Image files
from PIL import Image
from urllib.request import urlopen
def main(inputs):
img1_url = "https://github.com/w3ichen/static/blob/main/image_file.jpg?raw=true"
img1 = Image.open(urlopen(img1_url))
img2_url = "https://source.unsplash.com/random"
img2 = Image.open(urlopen(img2_url))
return {"img1": img1, "img2": img2}